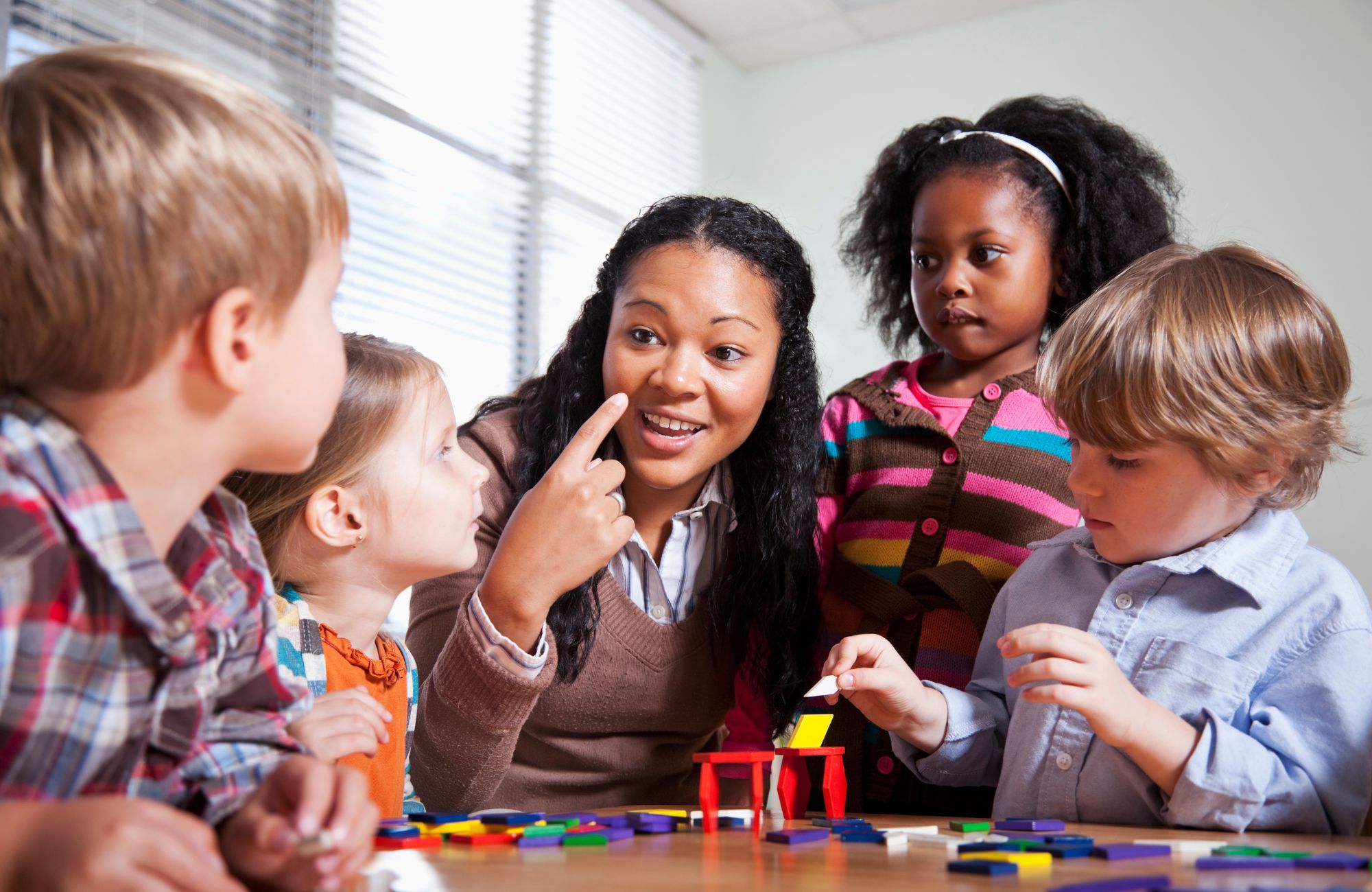
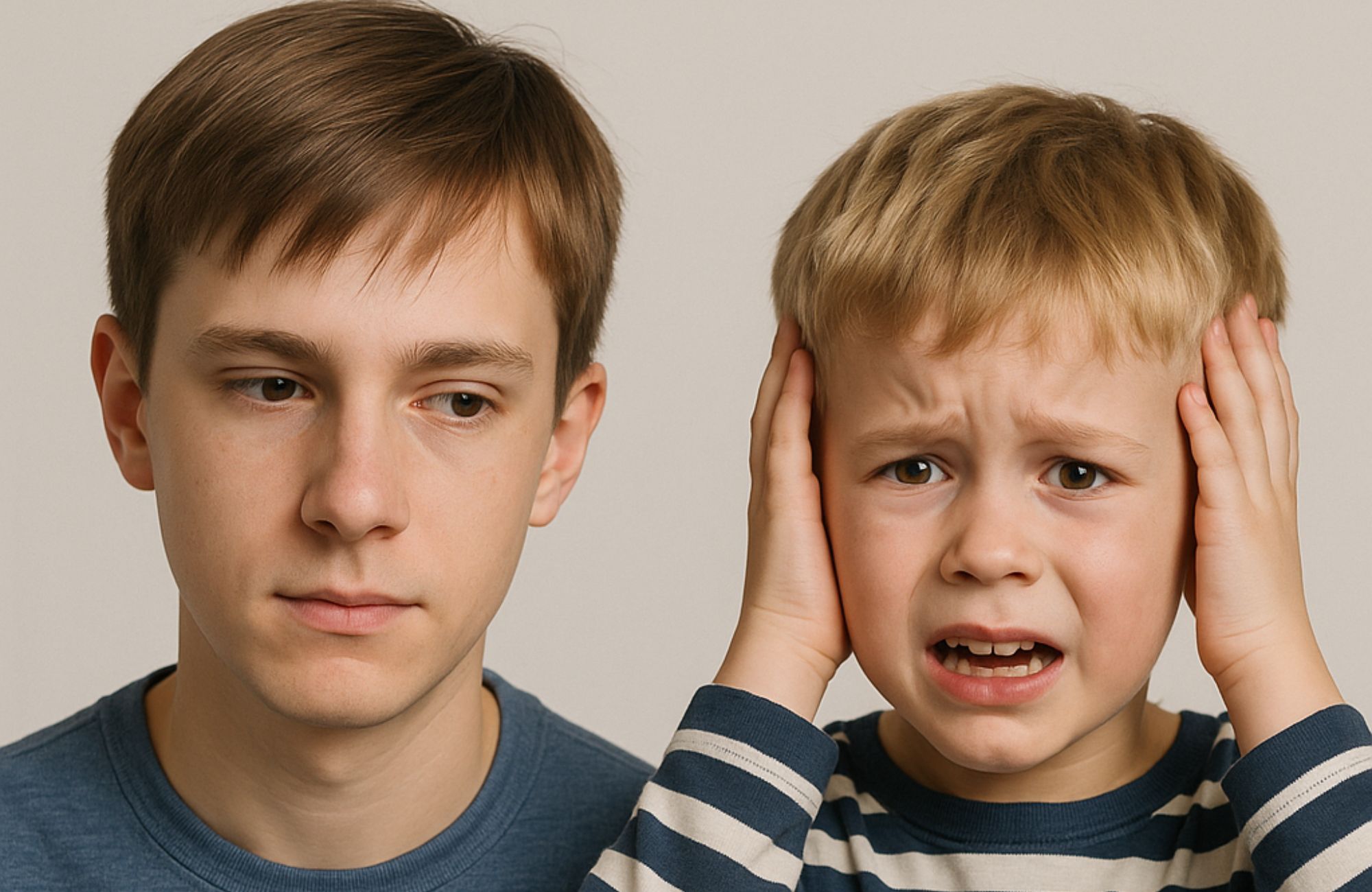
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a scientifically validated approach to understanding and modifying behavior. Widely regarded as one of the most effective treatments for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ABA therapy focuses on promoting positive behaviors and reducing negative ones. Through the use of evidence-based techniques, ABA helps children with autism develop new skills, improve their social interactions, and enhance their overall quality of life.
In this article, we’ll explore what ABA therapy does, how it works, its key benefits, and the important role ABA therapists play in transforming the lives of children with autism.
How ABA Therapy Works
ABA therapy works by breaking down complex behaviors, including the target behavior, into smaller, more manageable parts and teaching them step-by-step using reinforcement. Each behavior is reinforced through positive rewards, and unwanted behaviors are minimized through strategic interventions.
Key Techniques Used in ABA Therapy
ABA therapists use a variety of techniques to help children with autism acquire essential skills and reduce problem behaviors. Here are some key methods:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): This structured technique focuses on breaking tasks into small, achievable steps. Each step is reinforced to encourage mastery, building a foundation for more complex behaviors.
- Natural Environment Training (NET): A more naturalistic approach that takes place in everyday settings, NET helps children learn behaviors through real-life interactions, ensuring skills are generalizable.
- Positive Reinforcement: This is one of the core principles of this therapy. Positive reinforcement encourages desired behaviors by providing immediate rewards, such as praise or tokens.
- Prompting: ABA therapists use various forms of prompting (e.g., verbal, visual, physical) to guide children in completing tasks. Over time, these prompts are faded to promote independence.
Benefits of ABA Therapy for Children with Autism
This therapy has proven to be highly effective in helping children with autism and other developmental disorders develop new skills and improve their overall quality of life. Below are some of the key benefits:
1. Skill Development
ABA therapy helps children develop a wide range of skills, including:
- Social Skills: Children with autism often struggle with social interactions. ABA therapy teaches them how to communicate, share, and engage appropriately with peers and adults.
- Communication Skills: Whether verbal or non-verbal, ABA therapy helps children with autism develop both receptive (understanding language) and expressive (speaking or using gestures) communication skills.
- Life Skills: ABA therapy focuses on teaching children essential life skills, such as self-care (dressing, eating), problem-solving, and daily routines.
2. Behavioral Improvements
ABA therapy is instrumental in reducing challenging behaviors like tantrums, aggression, and self-injury, which can be common in children with autism. By using positive reinforcement, children learn to replace these negative behaviors with more appropriate alternatives.
- Behavior Reduction: ABA therapy helps children replace inappropriate behaviors with more functional ones.
- Increased Independence: Through skill-building, children with autism learn to do more things on their own, which fosters greater independence in their daily lives.
3. Early Intervention Benefits
Research shows that early intervention with ABA therapy leads to better long-term outcomes for children with autism. The earlier children begin therapy, the more likely they are to acquire essential skills and improve their social functioning.
The Role of ABA Therapists
ABA therapists are trained professionals who specialize in applying ABA principles to teach children new skills and address challenging behaviors. They work closely with the child, the family, and other professionals to create individualized treatment plans. Here’s what ABA therapists do:
Responsibilities of ABA Therapists
- Design and Implement Treatment Plans: ABA therapists create personalized treatment plans based on each child’s unique needs and goals.
- Use ABA Techniques: They employ techniques like positive reinforcement, discrete trial training, and prompting to help children succeed.
- Monitor Progress: ABA therapists collect data on the child’s progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure continued improvement.
- Collaborate with Families: ABA therapists work closely with parents and caregivers to ensure that the skills learned in therapy are carried over into everyday life.
Importance of BCBA Certification
Most ABA therapists are certified by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB), ensuring they have the necessary training and expertise to provide high-quality therapy. To become a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA), a therapist must complete advanced education, supervised experience, and pass a national exam.
Communication Skills Development Through ABA
One of the greatest strengths of ABA therapy is its ability to help children with autism improve their communication and emotional skills. Many children with autism struggle with both verbal and non-verbal communication, which can lead to frustration and behavior issues. ABA therapy addresses this gap in communication, helping children express themselves more effectively.
How ABA Therapy Supports Communication
- Expressive Language: ABA therapy teaches children to communicate their needs and wants through speaking, gestures, or written forms.
- Receptive Language: Children also learn to understand language, follow directions, and comprehend instructions.
ABA therapy plays a significant role in helping children with autism bridge the communication gap, enhancing their ability to interact with others.
Insurance Coverage for ABA Therapy
ABA therapy is often covered by insurance, especially when provided by a trained behavior analyst, but coverage varies by provider and location. Many private insurance companies, as well as Medicaid, provide coverage for ABA therapy, particularly for children diagnosed with autism.
What Does Insurance Cover?
- Health Insurance: Many private insurance plans cover ABA therapy services, although the specifics can vary.
- Medicaid: Medicaid often covers ABA therapy for children with autism, depending on state regulations.
- State Mandates: Some states have laws that require insurance companies to cover ABA therapy services for children with autism. Families should check their state’s mandates to see what is covered.
Finding ABA Providers
Finding a qualified ABA provider, such as your child’s ABA therapist, is crucial for ensuring your child receives the best possible care. Here’s how you can find the right ABA therapist for your child:
Steps to Find ABA Providers
- Research Online: Look for certified ABA providers in your area, ensuring they are accredited by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB).
- Ask for Referrals: Talk to other parents, healthcare providers, or autism organizations for recommendations.
- Evaluate Providers: Interview potential providers and ask about their experience, treatment strategies, and approach to ABA therapy. You may also want to observe a therapy session before making a decision.
Conclusion
ABA therapy is a powerful tool for helping children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) develop essential skills, improve social interactions, and reduce problem behaviors. Through evidence-based techniques like positive reinforcement and discrete trial training, ABA therapists can provide children with the necessary skills and tools they need to succeed in everyday life. If you’re considering ABA therapy for your child, it’s important to find a qualified provider who can tailor a treatment plan to meet your child’s unique needs and ensure continued progress.
At Affinity ABC, we understand the importance of ABA therapy in helping children with autism thrive. Our team of experienced therapists is here to guide your child through personalized ABA therapy sessions tailored to their unique needs. Contact us today to learn how ABA therapy can make a meaningful difference in your child’s life.
FAQs
What is the purpose of ABA?
The purpose of ABA therapy is to promote positive behavior change by teaching new skills, including academic skills, improving communication, and reducing undesirable behaviors in children with autism.
What are the main points of ABA therapy?
ABA therapy focuses on breaking down complex behaviors into manageable parts and using techniques like positive reinforcement and discrete trial training to encourage new learning skills and reduce challenging behaviors.
What do you do during ABA therapy?
During a typical ABA session, children work with trained therapists on activities such as communication exercises, social skills practice, and behavior management techniques. Sessions are individualized based on the child’s needs.
What are the pros and cons of ABA therapy?
ABA therapy has many benefits, such as improving social skills and reducing problematic behaviors. However, it can be intensive and requires commitment from both the child and their family, along with a therapist who has a master’s degree, to be effective in the long term.